The more I think I know something about Operation Overlord and Operation Neptune, the famed Normandy landings of World War II, the more I realize that I have only scratched the surface in understanding the most complex operation in military history.
The incredible effort that went into the preparations for the D-Day landings is staggering. The monumental logistics required to put the men and equipment on a hostile beach in France are often overlooked.
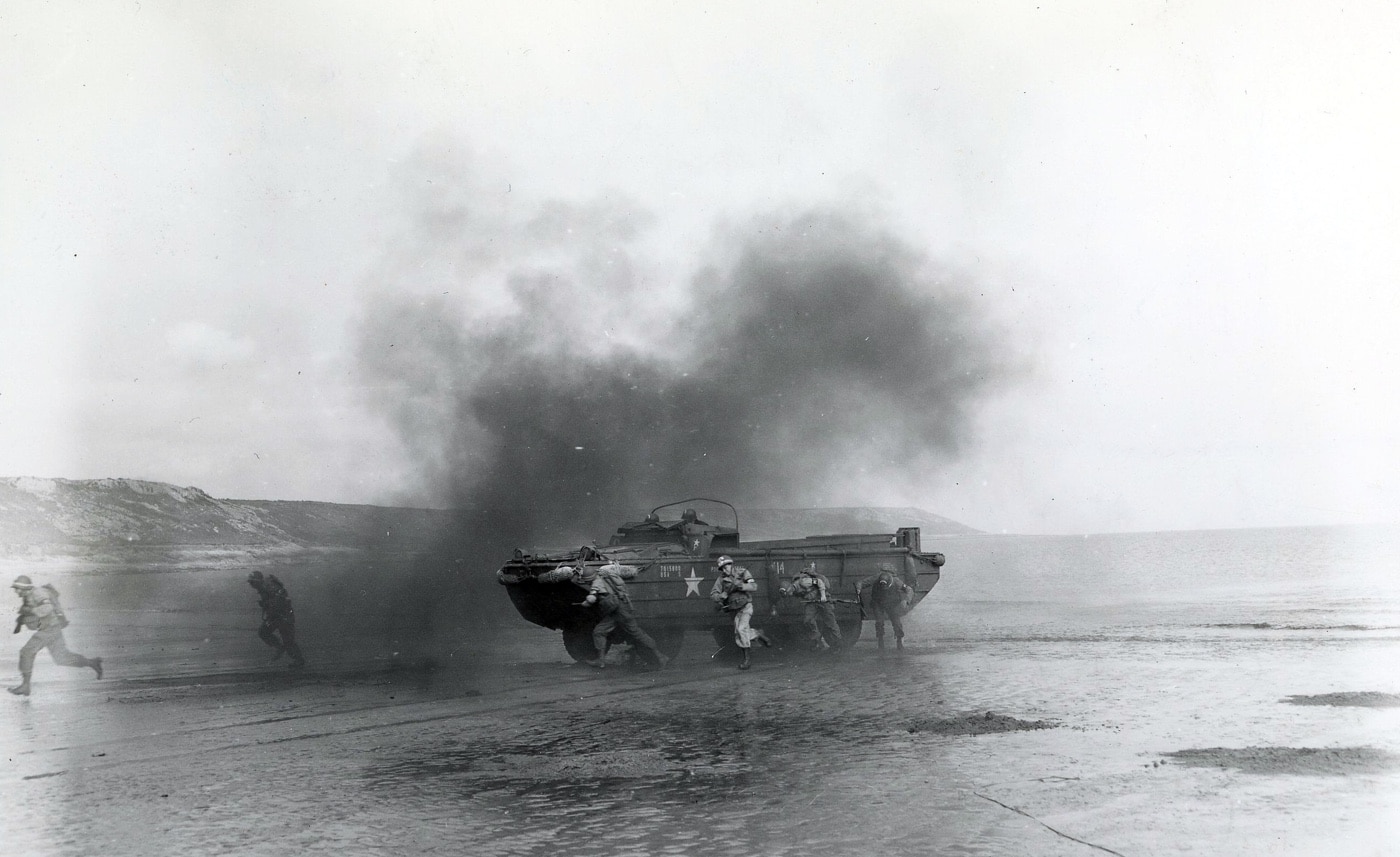

On the morning of April 28, 1944, as the ships of Convoy T-4 prepared to participate in “Exercise Tiger”, a large-scale rehearsal for D-Day, the fog of war settled in, and real-life events conspired to make the practice into a brutal introduction to the realities of the war.
Horrible Invasion Rehearsal
After the war, captured German documents revealed that Luftwaffe and Kriegsmarine reconnaissance had identified a large group of Allied ships, including capital ships and many troop transports, gathering at the harbors of Portsmouth, Pagham, Chichester, Langstone and Exbury. Around Southampton, German intelligence identified hundreds of trucks and other military vehicles, and German radio intercepts indicated that a large operation was underway.
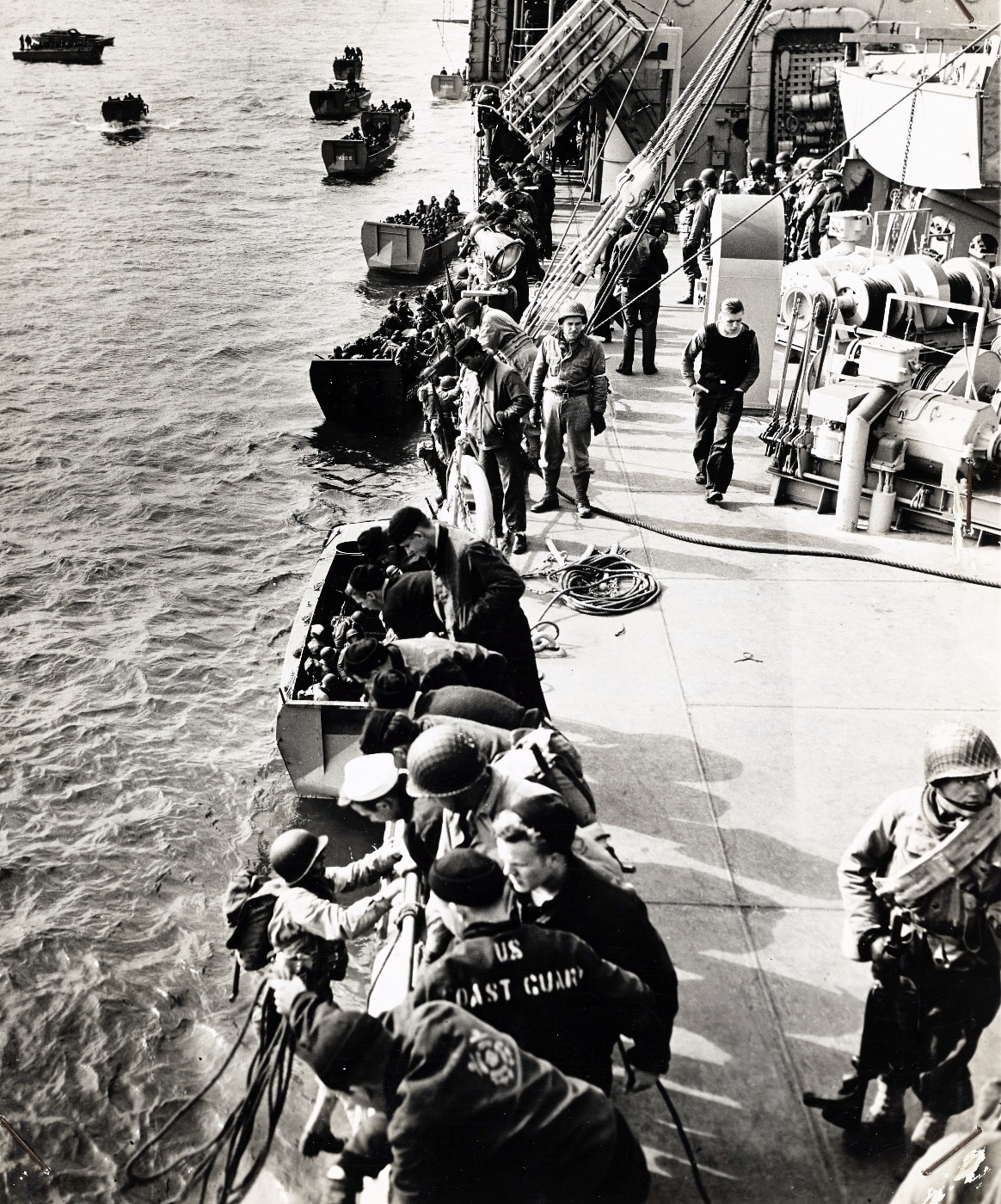

What the Germans found by April 25, 1944, were the preparations for Exercise Tiger, a massive invasion rehearsal that would see several convoys of ships operating in the waters of Lyme Bay — the “rehearsal beaches” on the coast were chosen for their similarity to the targeted invasion beaches in Normandy.
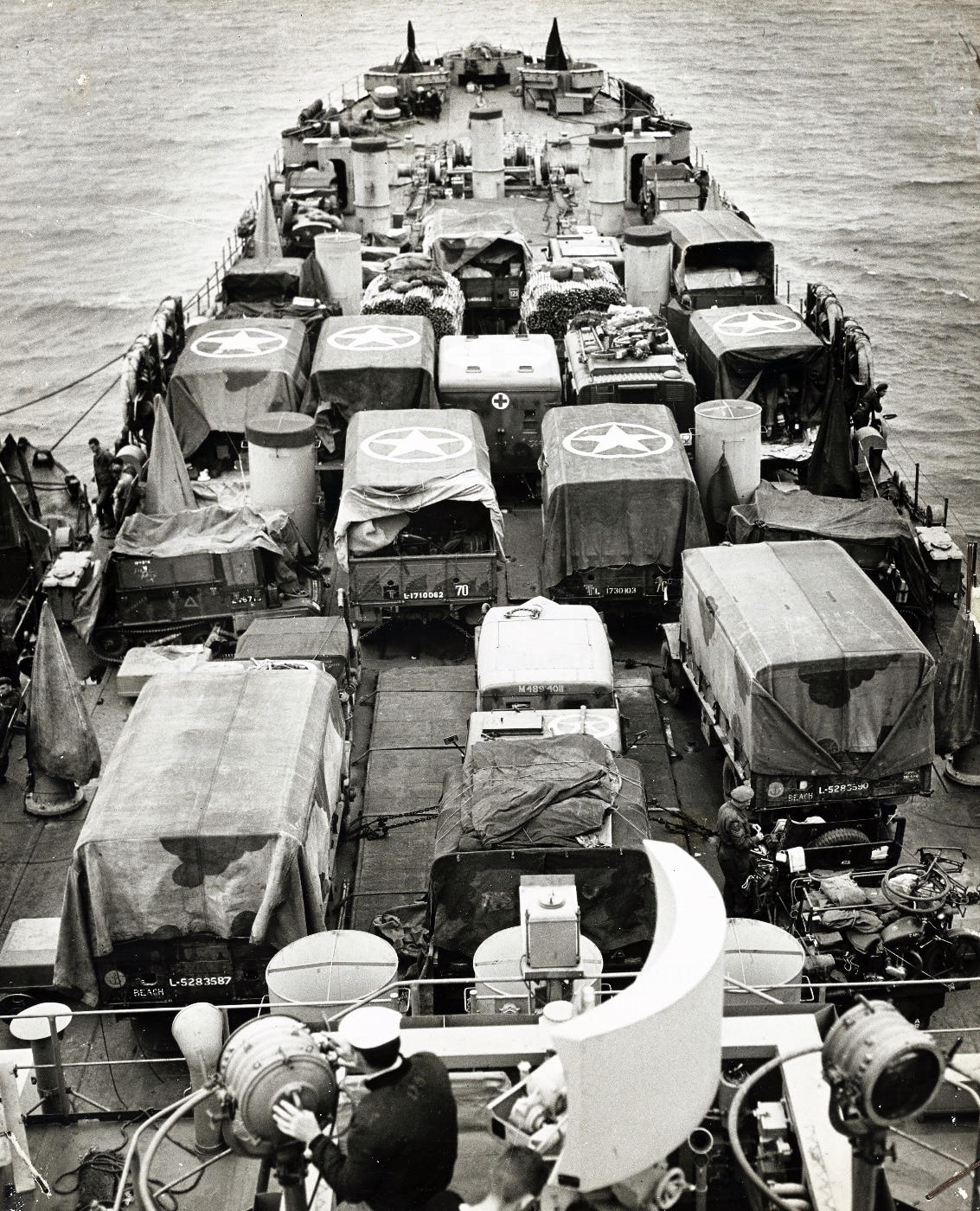

The war history of the U.S. 5th Engineer Special Brigade provided this description of the Americans’ temporary home and training grounds for their “friendly invasion” of England:
“Thousands of Yanks know this part of Devon, chosen because of its resemblance to the Cherbourg coast, almost as well as their own hometown. The area comprises the villages of Strete, on the brow of a 350-foot cliff, and Slapton, just 50 feet above sea level — these two bore the brunt of the constant assaults. Almost all the windows in the villages were broken, although the blasts played their usual tricks, and some glass porches and hot houses remained intact next to shattered houses.”
Spotted by German Recon
On April 24, 1944, eight LSTs (Landing Ship, Tanks) gathered to form Convoy T-4, and they slowly approached Lyme Bay. On board the massive transport ships, the tanks and wheeled vehicles were filled with fuel and ammunition to provide realistic conditions for the invasion exercise.
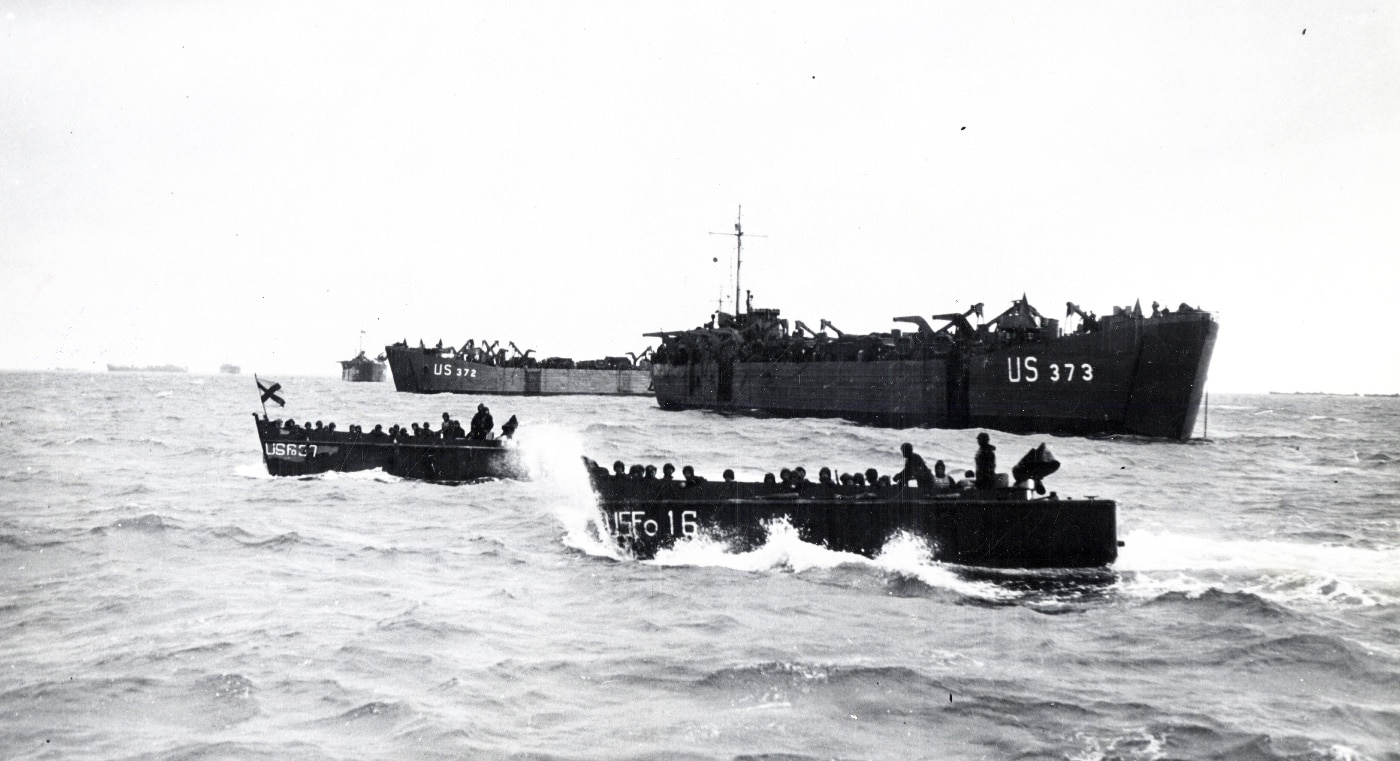

On the 25th, as the LSTs were entering Lyme Bay, they were spotted by German recon aircraft — and their photos showed German intel officers the significant build-up of ships, military vehicles and men at Portsmouth, Spithead, Southampton, as well as Pagham, Chichester, Langstone, and Exbury. The Germans also intercepted enough radio transmissions to confirm that something significant was going on in the area.
Convoy T-4 in Lyme Bay: Confusing Cloud of Secrecy
Convoy T-4 started off with only two escorts — the destroyers HMS Scimitar and HMS Azalea. Unfortunately, the escorts were quickly reduced by half as the Scimitar collided with an American LST outside Portsmouth. It took some time for HMS Saladin to steam out to replace her, and did not arrive in time to protect the convoy.
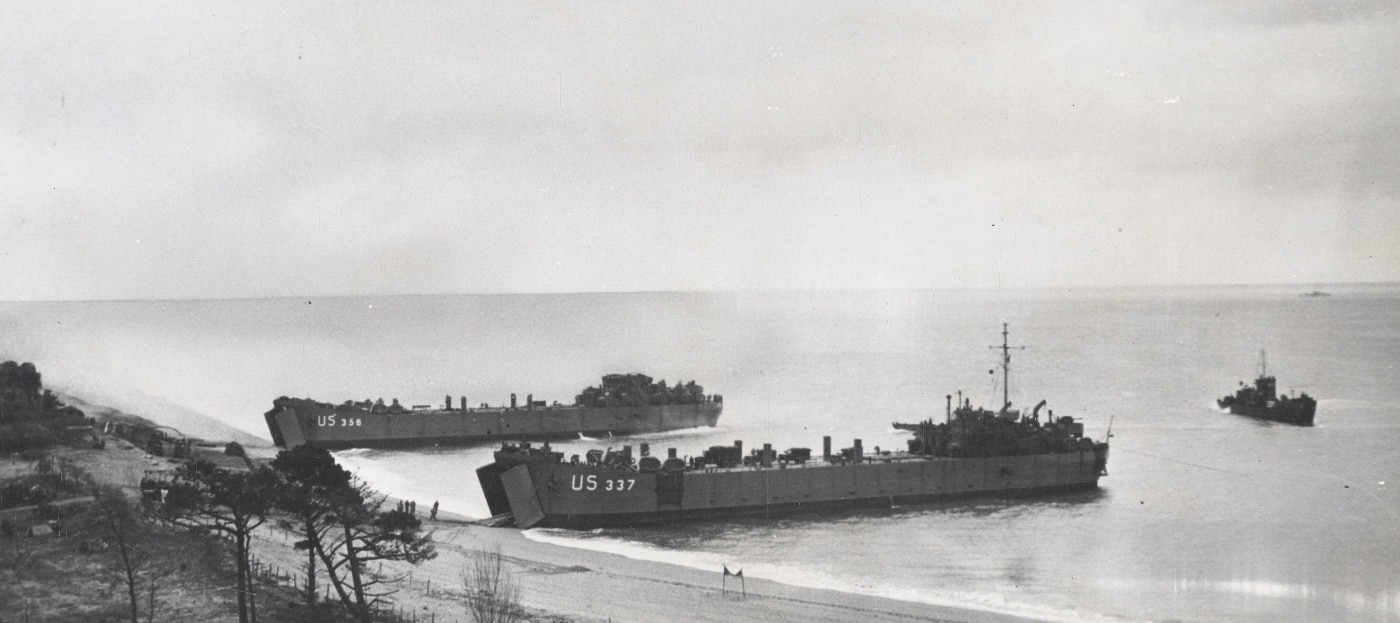

While the escorts and the American transport ships had been briefed on a potential E-boat (German torpedo boats) threat, the individual ship commanders were particularly sensitive to the secret nature of the training operation. There were several men aboard the convoy who knew the timing and plans for Operation Overlord.
The German torpedo boats were actually spotted in the overnight hours as they approached the bay and British radar picked them up. The E-boats were also spotted at a distance by lookouts on the LSTs. Nothing was done.
A little later, British coastal gun crews spotted the German boats but held their fire. The destroyer Azalea was told, but did nothing. An overabundance of caution, focused on radio silence, was exacerbated by the use of incorrect radio frequencies between U.S. Navy and Royal Navy ships.
The Kriegsmarine Begins Its Attack
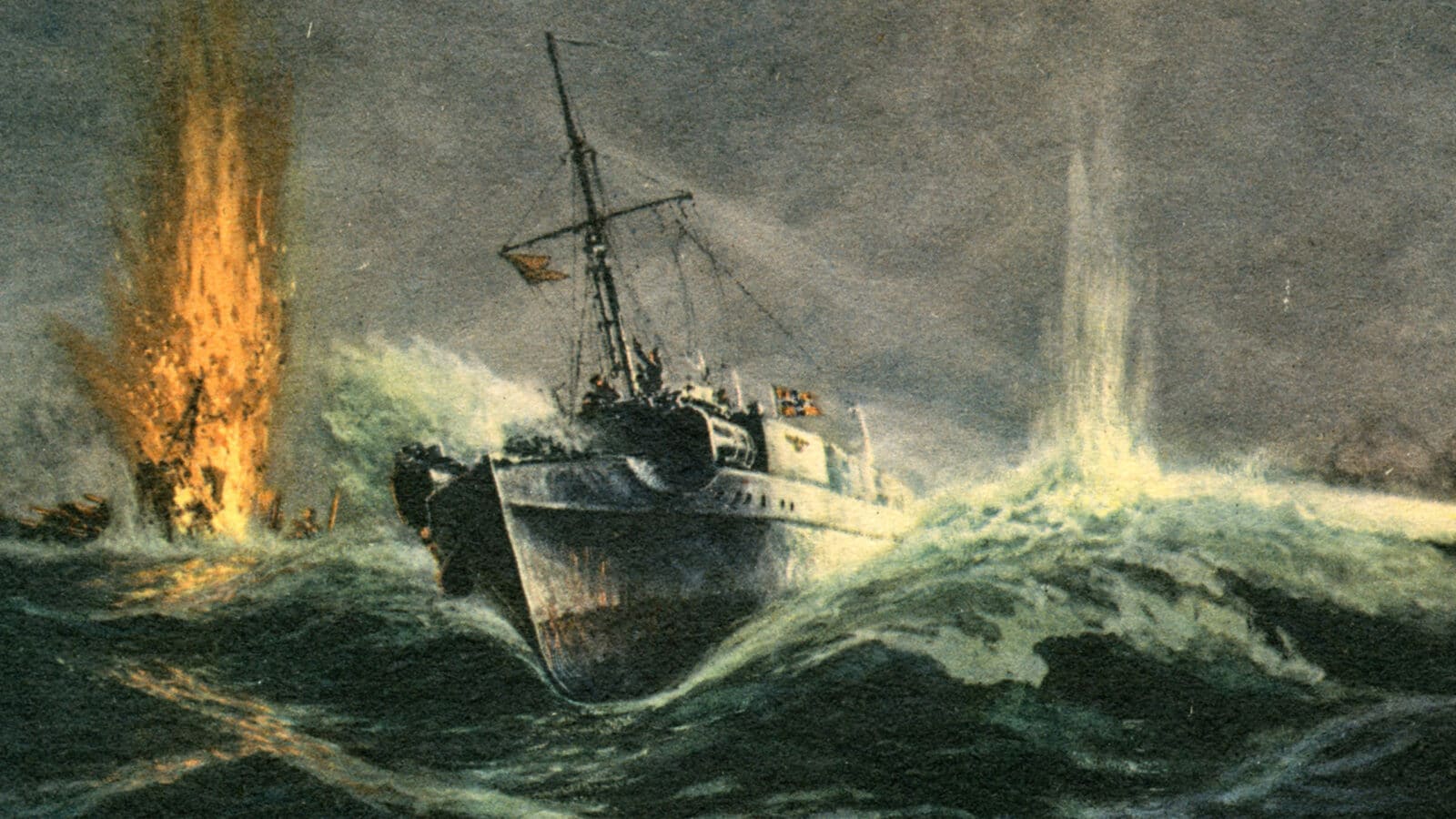
By 1:30, the S-Boots began their attack, firing their automatic cannons and launching torpedoes.
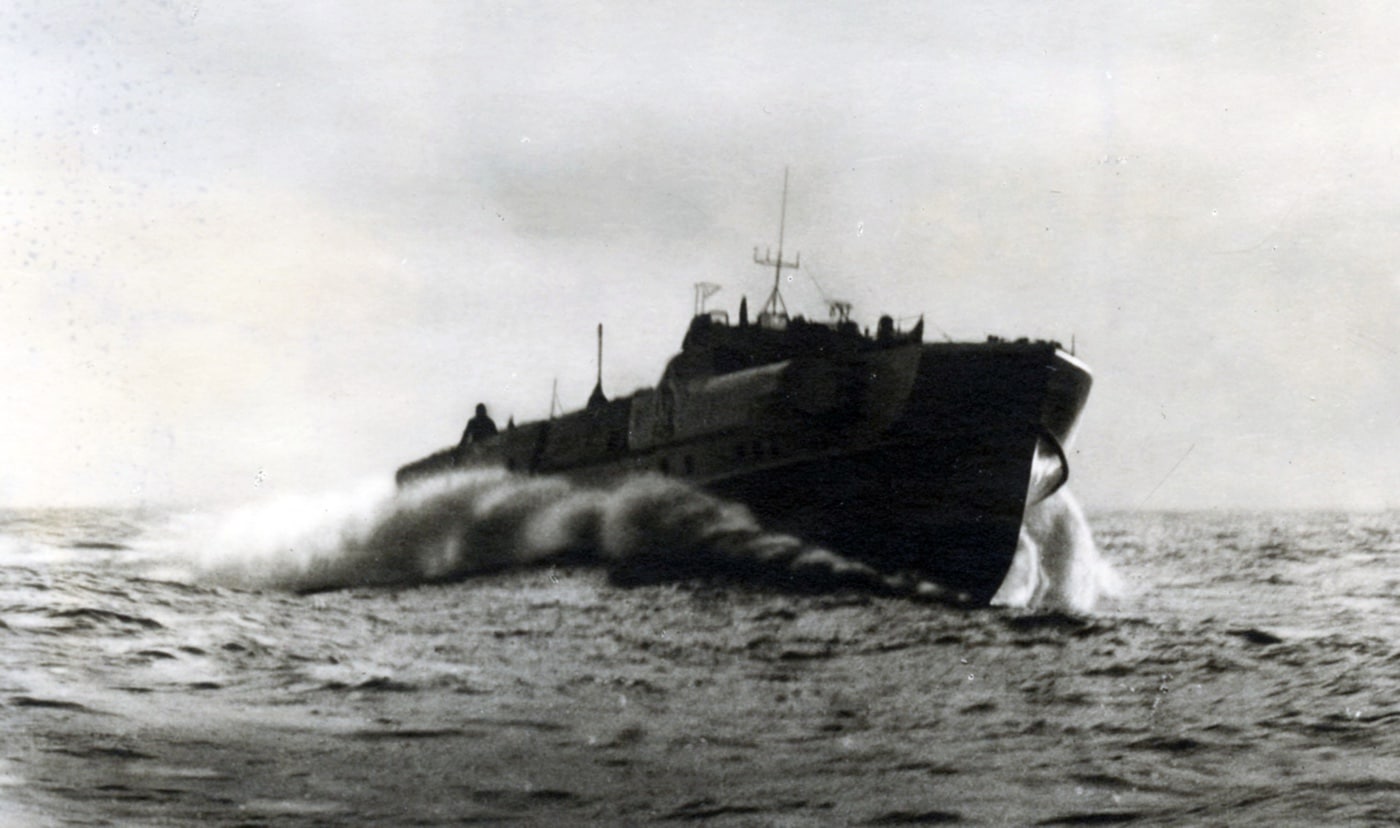

LST-507 was hit in its auxiliary engine room and quickly caught fire — the fully fueled vehicles aboard burned furiously while ammunition cases exploded. Green troops ready for amphibious training were not properly prepared to abandon a burning ship. Many were still wearing full packs and overcoats when they went into the water, and most of them quickly drowned.
About 45 minutes later, LST-531 exploded and sank within 10 minutes, with 467 men dying with her.
Shortly after, LST-489 was hit, losing her rudder and sustaining significant casualties.

With the water temperature at about 40 degrees, survivors struggling in the water were soon to be overcome by hypothermia.
Nearly 1,000 Casualties
In all, four LSTs bore the brunt during the attack. LST-289 was torpedoed and damaged, but returned to port. LST-507 was torpedoed and sunk. LST-511 was damaged by friendly fire, but returned to port. LST-531 was torpedoed and sunk.
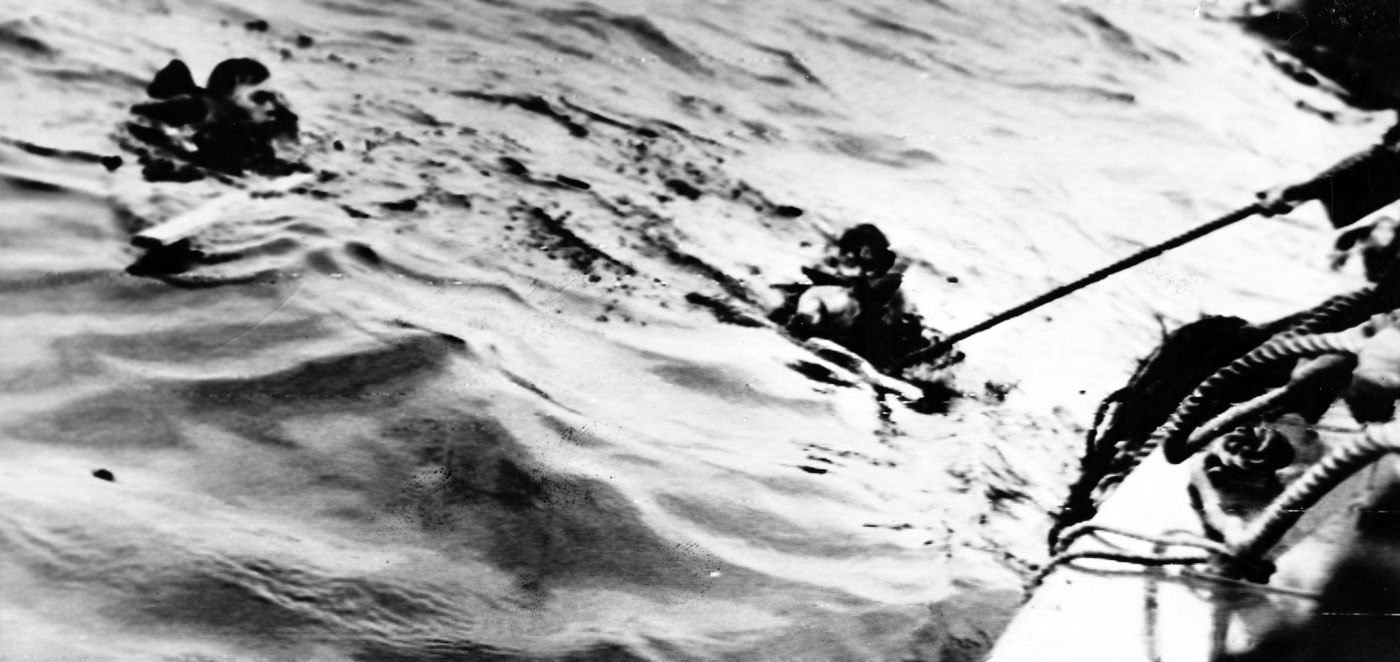

The cost was incredibly high, and the six boats of the 5th S-Boot Flotilla got away cleanly. The LSTs had been travelling in a straight-line formation, and the use of just a single escort conspired to make it rather easy for the German torpedo boats.
The confluence of errors and miscommunication conspired to place Convoy T-4 dramatically in harm’s way, and a level of danger not even found during the actual D-Day landings. The grisly final accounting shows that 749 U.S. soldiers and sailors lost their lives that day, and more than 200 were wounded.
Lyme Bay Lessons
With D-Day just a few weeks away, the lessons learned from the disaster at Exercise Tiger, and the proposed remedies, needed to be swiftly implemented.
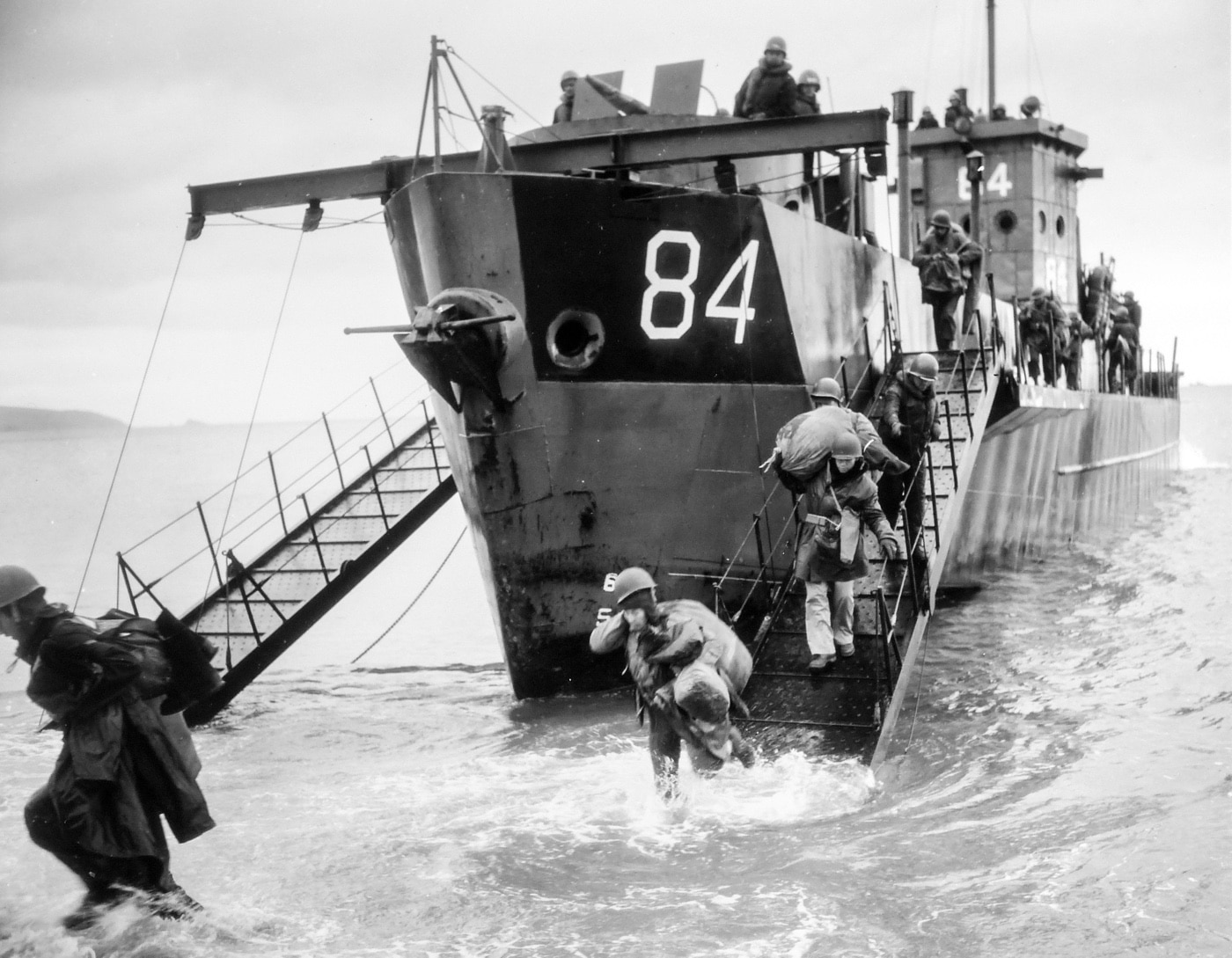

Communications between U.S. Navy and Royal Navy were standardized. The infantrymen headed to the beach were given more complete training in the use of lifejackets. It was a small change, but one that certainly had a positive effect on morale.
A group of light boats were also detailed to pick up survivors of sunken ships during the landings. Most importantly, there was a renewed focus on fighting off German coastal forces, particularly the deadly S-Boots.
Germany’s Fast Attack Craft: The S-Boots
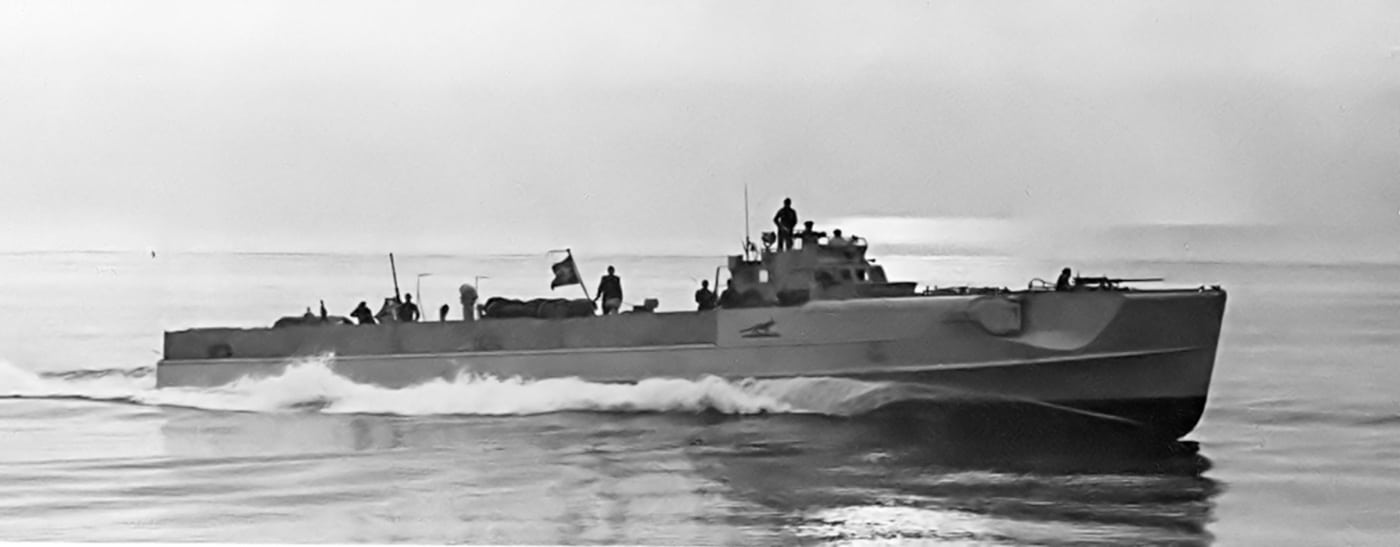
While U-boats captured much of the attention and gained most of the headlines, Germany’s fast-attack torpedo boats, the “Schnell boats” or “S-Boots” were quietly one of the Kriegsmarine’s most effective weapons. Once the German navy gained the French ports on the English Channel, any shipping along Britain’s eastern coastline was in danger.
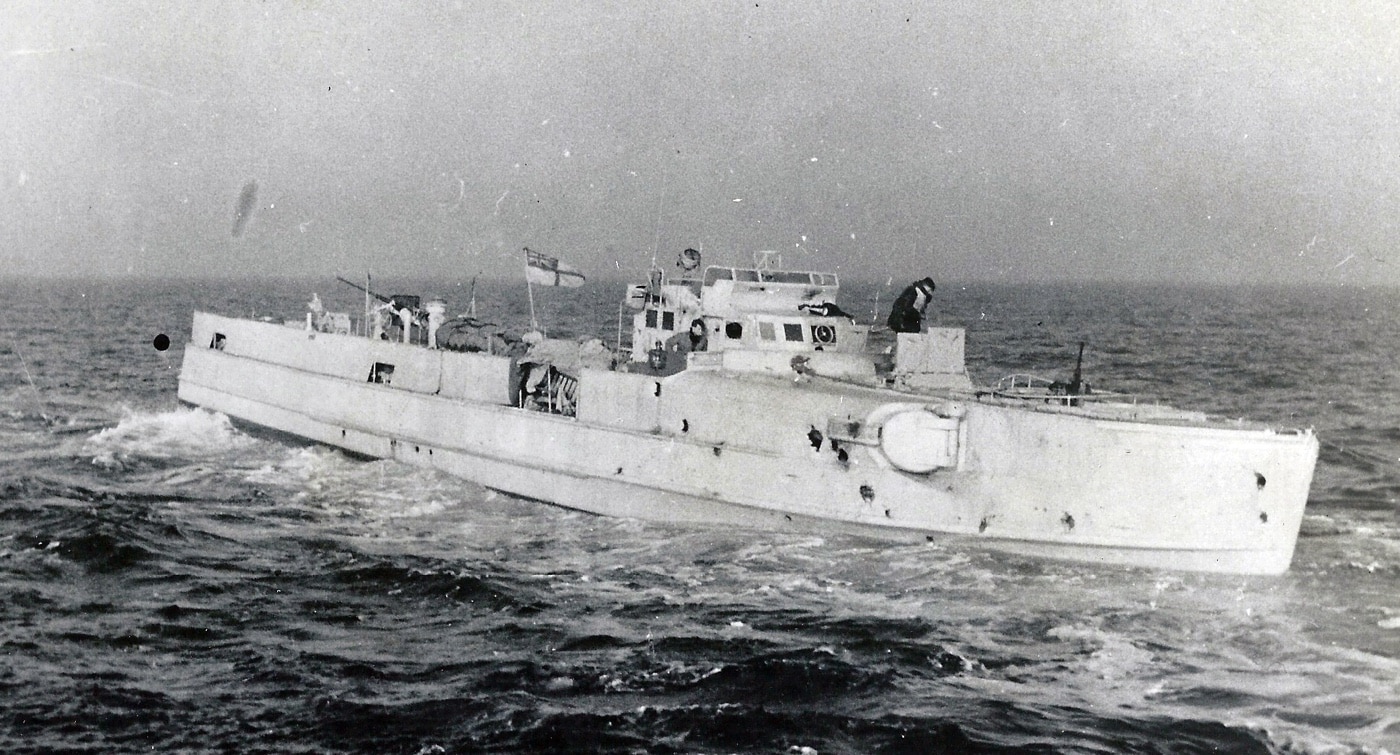
The existential threat from the S-Boots in the Channel led the Royal Navy to develop and maintain a significant Motor Gun Boat (MGB) force. Pitched battles between the fast-attack forces were regular events, and by the spring of 1944 the S-Boots remained a persistent threat.
During April 1943, German Admiral Donitz commented on the evolving dynamics of the Channel forces: “Against the constantly improving enemy defenses, the S-Boot can only remain effective if it continues to operate as a sufficiently large force. The development of S-Boot tactics therefore follows the same path as U-boat tactics. In the Channel, the boats are used now only in packs.”
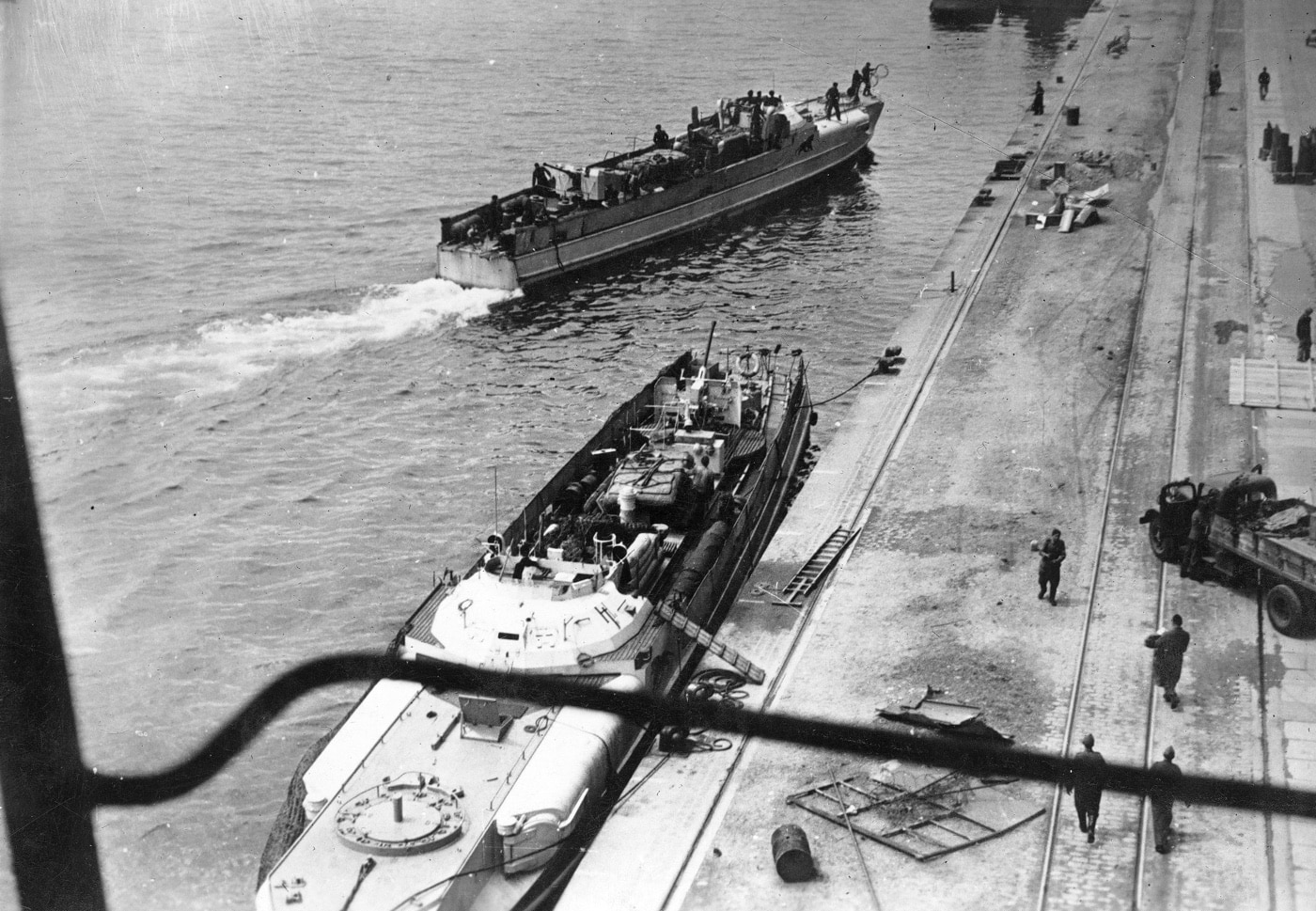

By 1944, the S-Boots carried progressively heavier armament. Many boats carried a 37mm automatic cannon (or a 40mm Bofors) in the aft positions, while a few carried a quadruple 20mm Flak 38. In the bow, a 20mm Flak was mounted in the forward turret, while various single and twin MG34s provided additional AA firepower.
The boats carried two fixed, forward firing torpedo tubes, with the pair of reload torpedoes carried on a bed of ball bearings, to be easily rolled into place. G7a torpedoes were carried throughout the war. On mining missions, the torpedoes were replaced by six mines. The diesel-engine S-Boots could sustain a speed of about 43 knots and accelerate up to 48 knots (nearly 55 mph) for short periods. Their range was excellent — up to about 850 miles.
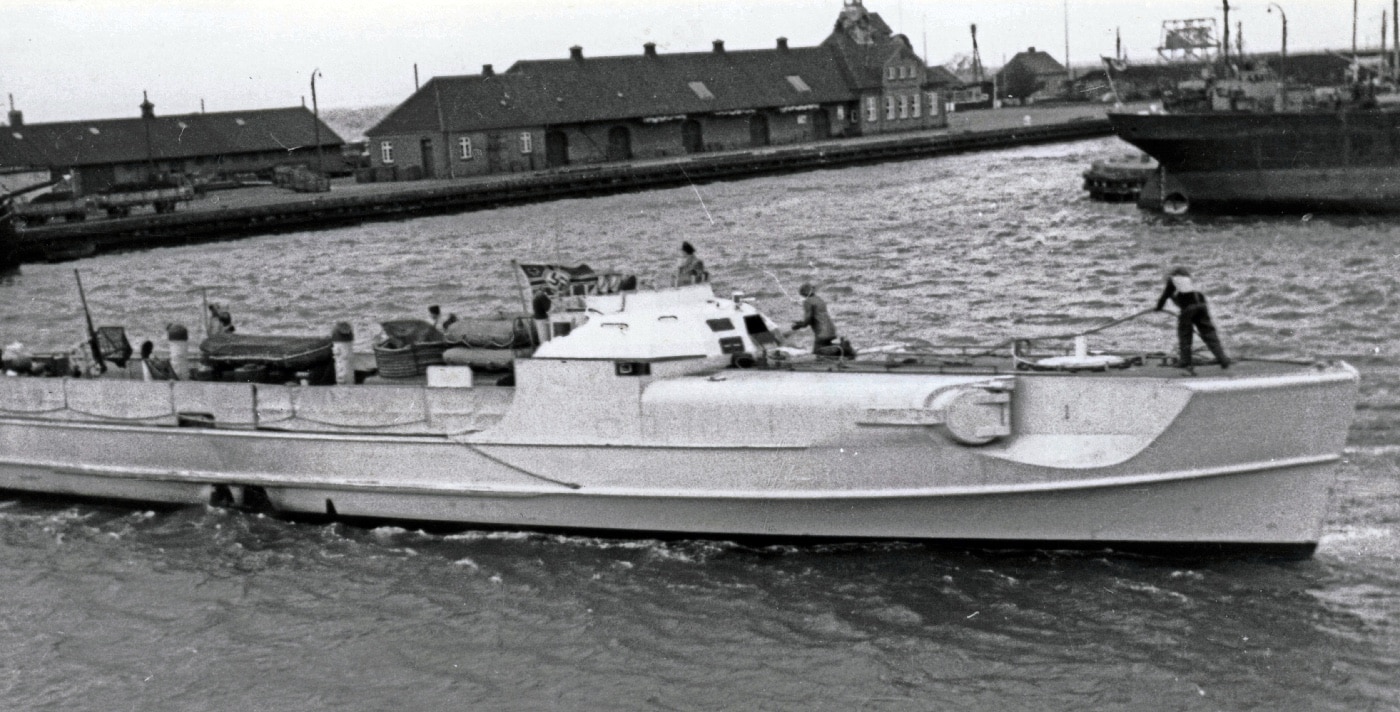
Prior to the invasion there was often a crippling lack of cooperation between the Wehrmacht, Kriegsmarine and Luftwaffe. The Germans placed great faith in their reconnaissance ability, but no one seemed quite sure who would provide the nearly two-week advance notice of any Allied invasion convoy sailing across the English Channel that German defenders were counting on.
As for the S-Boots, they planned to sow the exits to British invasion ports with mines, to delay and whittle down the seaborne invaders. The Luftwaffe and Kriegsmarine did not discuss the S-Boot success at Lyme Bay, and further investigation of the possible connection between the practice landing beaches in England and the connection with the Normandy area were not pursued.
Hidden Realities
While the tragedy of Slapton Sands was never officially “covered up,” the events of that top secret exercise were not discussed, particularly with the massive D-Day operations coming so soon after. When the war was won, no one was inclined to ruin the celebratory mood by detailing the actions of a bloody failure.
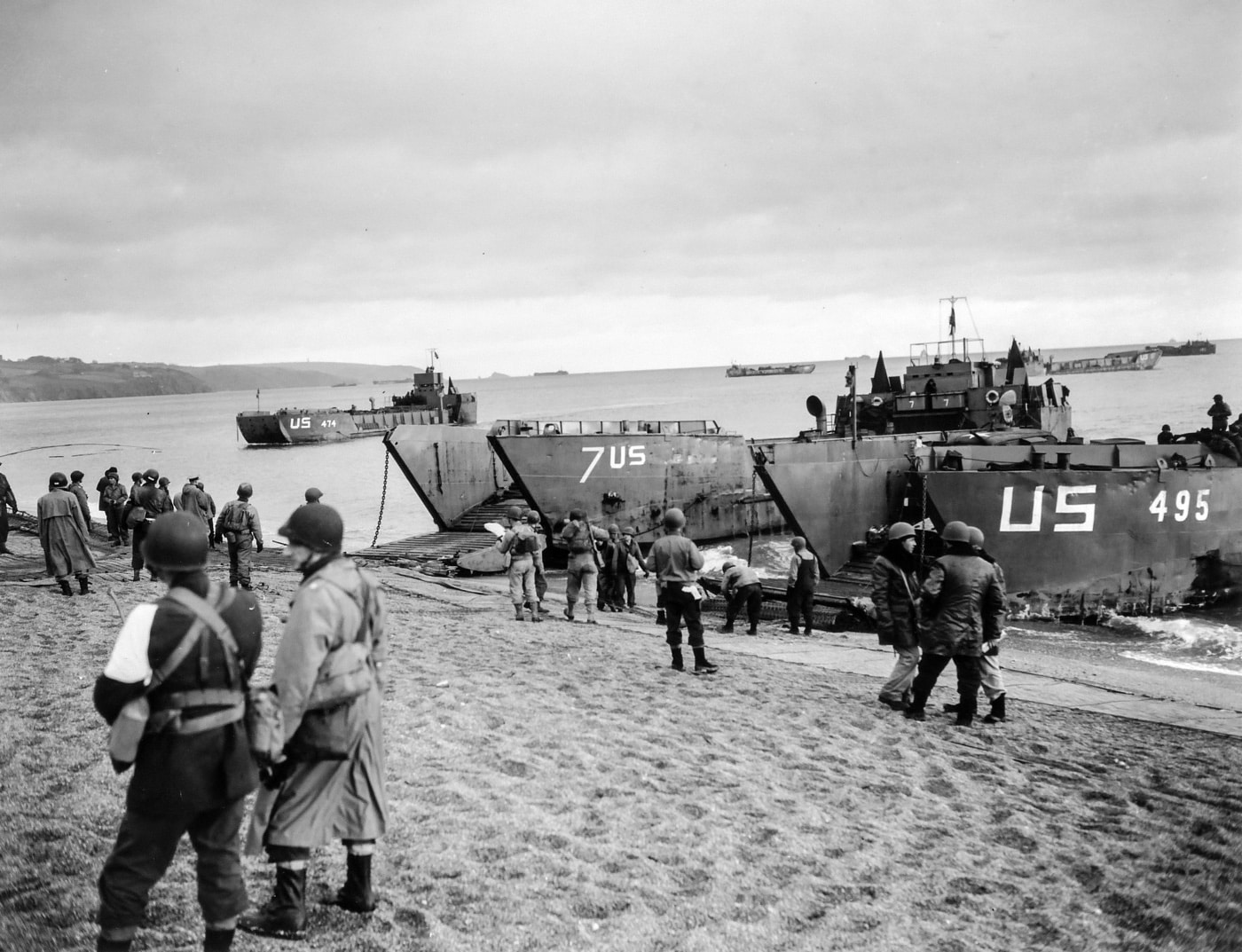

I searched for first-hand information about the action in Lyme Bay, and the following excerpts come from the war report of the USS LST 289:
USS LST 289
Report of action and damage
27 April 1944: At 0104, there were two slight jars felt, about 30 seconds apart — similar to the effect of depth charges at a distance. At 0130 gunfire was observed directed at (LST) 507, about 600 yards astern of us. In the opinion of myself and my gunnery officer it appeared to be 40mm from 2500 to 4000 yards distance, and coming from almost due west, but at no time did anyone see the craft firing…at no time were any flashes observed, making it futile to return the fire.
When we were attacked, we were manning one bow and one stern 40mm, after which we immediately went to general quarters. The firing lasted about 10 minutes and we received no hits out of two or three hundred rounds fired. Shortly after the firing ceased the 507 came back into formation about 700 yards astern of us. At 0203 there was an explosion amidships on the starboard side of the 507, with a great flash of flames that seemed to spread instantly from stem to stern.
Due to the full load of Army personnel for whom we were primarily responsible and our own vulnerability, we considered it unwise to go to the assistance of the 507.
AT 0228 four port 40mms and three 20mms opened fire at what some crews described as a fast white boat, similar to the British ML series, while others were firing at a torpedo wake coming from 315” relative, headed for a point one fourth of the way forward of the stern. The torpedo appeared to be going not more than 15 or 20 knots, and from the Super Conn it seemed that it was going to miss. It didn’t look to be a full-sized torpedo and it was quite close to the surface. It exploded with considerable flash and roar but did not shake the ship noticeably, only a few light bulbs had broken filaments and there were no strained ankles. The starboard stern 40mm tub was blown back on the number five boat davit, and the entire stern section aft the deck house was curled over and onto the navigation bridge aft the signal bridge. It struck sufficiently high that the screws were not damaged.
We had 395 Army officers and men aboard, with 22 “ducks” (DUKWs), a 2 ½ ton truck, and one Jeep. The Army personnel were orderly and cooperative throughout, acting as lookouts and manning the 20mm guns left by the small boat crews.
It is respectfully submitted that this experience has crystalized our ship’s company into an experienced fighting unit with a group morale of the very highest, all of whom have an intense desire to remain together, and upon their behalf I urge that their request be favorably considered.
I cannot speak too highly in praise of my crew, whose cool courage and efficiency during the hours of suspense and danger was worthy of the highest ideals of the U.S. Navy. The engine room watch calmly got the engines started after the explosion. The repair parties were phenomenal in their control of the fire. The small boat crews held up under hours of grueling seamanship. The line-handling parties worked to the point of exhaustion tending the towing lines. The medical corpsmen searched for hours through the hazardous wreckage for the injured. The gunners’ mates crawled throughout the ship in darkness scattered 40mm shells. Every officer was an example to the men in their cool execution of duty. There wasn’t a man who had a physical or nervous breakdown. I am proud of the privilege of being their commanding officer.
– Lt. Harry A. Mettler, U.S. Navy Reserve
Editor’s Note: Please be sure to check out The Armory Life Forum, where you can comment about our daily articles, as well as just talk guns and gear. Click the “Go To Forum Thread” link below to jump in!
Join the Discussion
Read the full article here









![Walther PDP Pro-X [HANDS-ON REVIEW] Walther PDP Pro-X [HANDS-ON REVIEW]](https://www.recoilweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/Walther-PDP-Pro-X-18.jpg)








Leave a Reply